Know About Taper Roller Bearings In Brief
There are many different types of bearings available today, each tailored to your requirements. A machine’s numerous moving components are supported in motion by bearings.
One of the most adaptable bearings in the business is a tapered cup and tapered cone, which are rolling element bearings that can handle and manage axial and radial forces.
For all of your produced ball and roller bearing products, ZNL bearings is dedicated to being a leader in the industry.
We reasoned that it would be beneficial to compile a list of postings that covered the many types of roller bearings you would require for your projects. Here are the first few articles—
—in case you missed them.
Tapered Roller Bearings: What Are They?
The rolling element bearings known as tapered roller bearings are capable of withstanding both axial (i.e., appropriate thrust bearings) and radial forces.
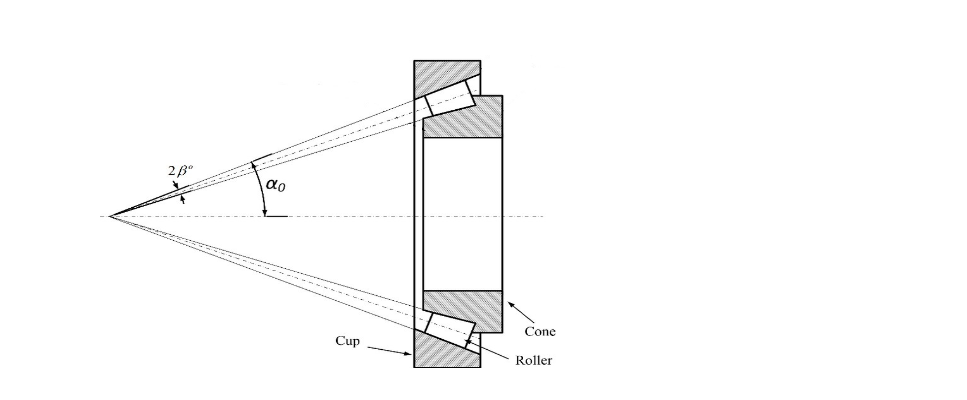
Conical raceway segments make up the inner and outer ring raceways. The roller axes are tapered so that if the raceways’ conical surfaces were projected, they would all converge at the bearing’s pivot axis. Due to this shape, there is no sliding motion between the raceways and the outer diameter of the rollers, therefore the motion of the cones remains coaxial.
Advantages Of Taper Roller Bearings At ZNL
- Reduce friction to lower the amount of heat produced.
- Directional loading can be supported with ease.
- The capacity to handle large radial and thrust loads beats needle roller bearings, spherical or cylindrical bearings.
- The majority don’t require any modifications to enable pure axial, pure radial, or any mix.
- possess a large load capacity.
- Less skidding or sliding when unloading thanks to proper rolling motion
- sources with minimal load needs
Disadvantages Of Taper Roller Bearings At ZNL
- Choosing a tapered roller bearing has drawbacks just like most other decisions.
- Misalignment can lead to damage that cannot be repaired. It might be wise to select an alternative choice, such as spherical roller bearings, if you are aware that the likelihood of misalignment is significant.
- Speed is a second significant drawback of tapered roller bearings. They are designed for faster operations, which, depending on the operation, can be a problem.
What Uses Are There For Tapered Roller Bearings?
- Wheel bearings in moving vehicles constantly experiencing radial and axial forces
- suitable for heavy-duty, moderate-speed applications that demand durability
- vehicle wheel bearings
- shafts for agricultural machinery
- plane fuel dispensers
- Reducers and engines
- railway wheels
- Mining
- more construction…
The friction and heat produced by earlier bearing designs frequently led to their failure; tapered roller bearings are intended to address this issue. The bearings are capable of dispersing loads because of their tapered shape.
The structure is made to support combination loads, like simultaneous axial and radial loads.
The bearing axis enhances rolling while decreasing friction since the raceway’s projected lines converge at this location.
Depending on the angle of contact, the load bearing capability can either increase or decrease. The contact angle increases as the slope increases.
For increased radial load capacity, they are typically employed in pairs, though in some high-thrust situations, two or even four rows may be joined into a single unit.
The combined tapered roller bearings transmit a significant amount of driving force to the wheels on both sides by preserving proper gear interlocking while supporting radial and axial loads (in both directions) simultaneously.
Components Of Tapered Roller Bearings:

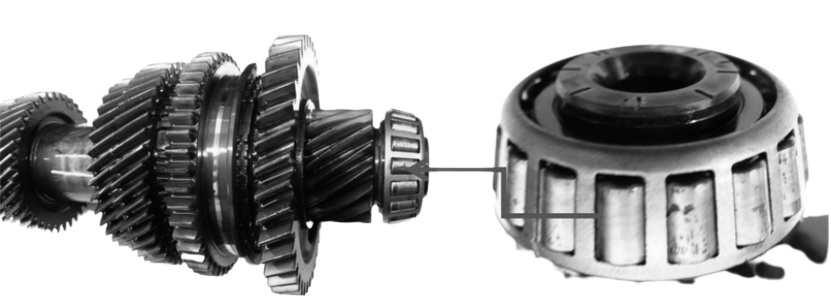
Cup and Cone: The outer ring on which the bearings rest is part of the cup. The inner ring, rollers, and cage make up the non-separable cone assembly. There is an angle in the raceways where the rollers move that matches the taper of the rollers. The outside raceway is known as a cup, and the inner raceway is known as a cone. In order to provide appropriate load distribution and smooth rotation, the cage, sometimes referred to as a retainer, separates the rollers. The slanted surfaces of the rollers, cones, and cups actively align the components of the machine; the cage is primarily responsible for holding the rollers together and distributing their spacing.
These bearings use tapered cylindrical rollers for axial and radial loads. The contact angle and the number of rows are the two factors that decide the type of load and the bearing capacity. It is possible to strengthen a bearing’s capacity to carry weights by increasing the number of rollers that it has in its internal structure.
The most popular type of cage is the CRCA steel cage, which is distinct from the cages used in other bearing types. The cage assists in spreading out the roller units as a component of the inner core assembly.
Between rollers and raceways, lubrication helps reduce friction, noise, heat, etc. There are several types of lubricants utilised, including synthetic oil, oil derived from petroleum, oil derived from silicone, greases, dry films, etc.
Seals effectively shield the bearing from moisture and other environmental irritants. The bearing’s ability to work properly may be hampered by impurities.
The requirements set forth for roller bearings must be met by tapered roller bearings.
A Compendium Of Specialized Industry Standards Has Been Developed:
- Tapered roller bearings designation system according to ISO10317
- Tapered roller bearing dimensions and limitations, following ISO 355
- Source: ABMA STD 19.1, which is the American Bearing Manufacturers Association’s standard for tapered bearings.
Why Do You Prefer This Bearing To Another?
In comparison to other types of roller bearings, Tapered roller bearings have unique design features. The term “tapered rollers” refers to the ends of the rollers, which have two different diameter sizes.
- The outer raceway is known as a cup.
- Its inner raceway is known as a cone.
Rolling raceways have an inclined surface that matches the taper of the rollers, giving these rings the appearance of cone segments.
A cage, called a retainer, keeps the rollers apart and ensures smooth rotation and load distribution.
The cage primarily serves to appropriately spread the rollers and contain them within the constructed assembly since the slanted surfaces of the rollers, cones, and cups actively align them.
The roller and cage assembly can’t leave the racetrack at high speeds because of a flange.
Maintenance
We are aware of the significant financial impact that downtime can have. You won’t need to look anywhere else for bearing repair services that can match your needs. Services for bearing repair decrease lead times and downtime, increase bearing life, and save money.
Closing Remarks
Tapered roller bearings reduce friction and heat, which can damage bearing structures. Industrial applications use this bearing for severe loads. Modification, production, and maintenance are just a few of the services ZNL offers to assist you in obtaining the bearings you require. Contact us (bearing specialists) to get started.









