Bearings play a crucial role in mechanical systems by minimizing friction between components that move and enabling smooth rotational or linear operations. While various types of bearings—such as deep groove ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, and cylindrical roller bearings—are built to handle different conditions, two major factors significantly affect their lifespan and efficiency: load and speed. At ZNL Bearings, we engineer our products to deliver exceptional performance under varying operational stresses, but understanding how load and speed interact with your bearings can make all the difference in machine reliability.
Understanding Load in Bearings
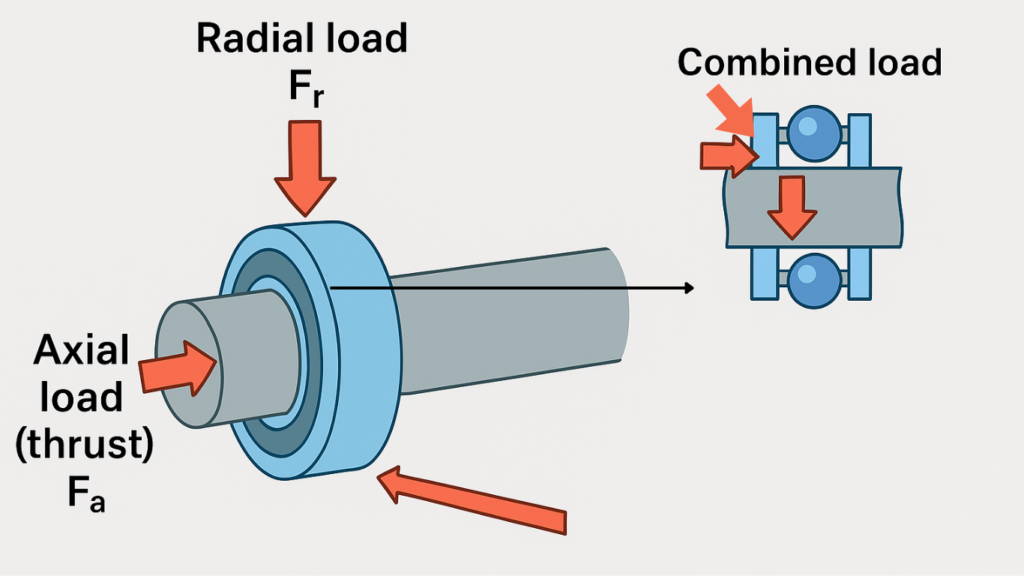
1. Types of Load
Load refers to the force exerted on a bearing. It is broadly categorized into:
- Radial Load: Consider it the force which acts at right angle to the rotating shaft.
- Axial (Thrust) Load: This force acts parallel or can say, is aligned along the shaft’s direction, that is axis of rotation, either pushing or pulling along its length.
- Combined Load: A mix of both radial and axial forces.
Different bearings are engineered to withstand particular kinds of loads depending on their structure and function. For example, deep groove ball bearings perform well under radial and moderate axial loads, while spherical roller bearings are ideal for heavy radial loads and misalignment conditions.
2. Effect of High Load on Bearing Life
Bearings are rated based on the expected fatigue life under a given load. Exceeding this load capacity—even for short durations—can lead to:
- Material fatigue
- Pitting and flaking
- Excessive heat generation
- Premature failure
At ZNL Bearings, our products are tested under real-world stress conditions to ensure optimal load capacity. However, proper load calculation and choosing the right bearing type are crucial for longer service life.
3. Dynamic vs Static Load Rating
- Dynamic Load Rating (C): The bearing’s capacity to withstand a variable or moving load over time. This is vital for rotating machinery.
- Static Load Rating (C0): Refers to the highest load a bearing can support in a non-rotating state without suffering lasting damage or deformation.
Overlooking these load limits may result in surface fatigue or damage, ultimately shortening the bearing’s operational life.
Speed and Its Impact on Bearings
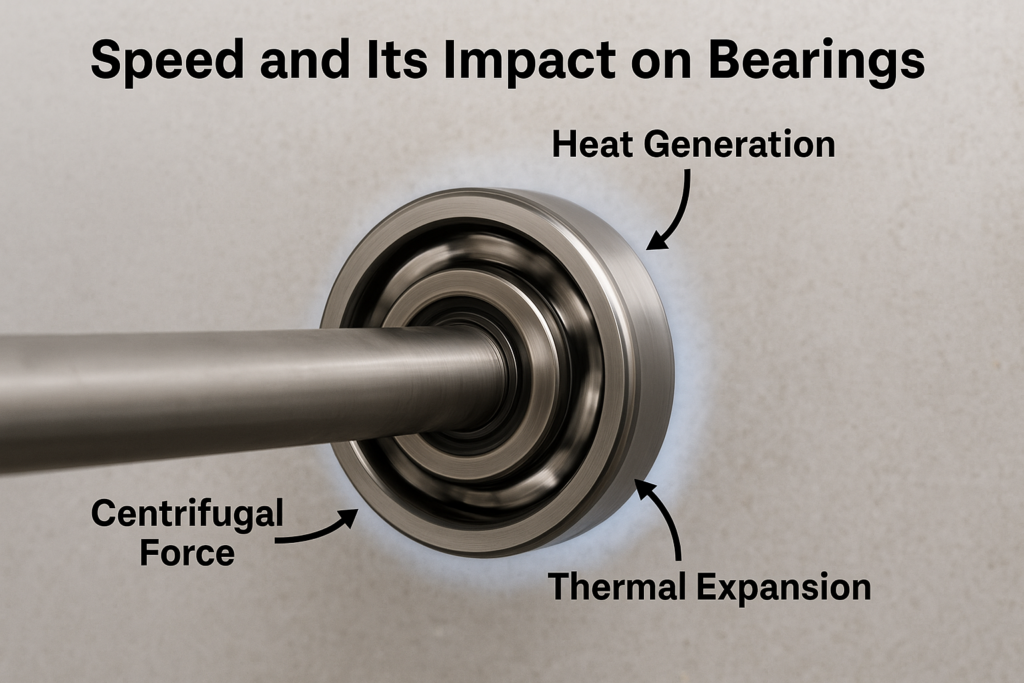
1. What is Speed in Bearing Context?
Speed in bearings is measured as RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). Every bearing has a limiting speed, which depends on:
- Type of bearing
- Lubrication method
- Load applied
- Heat dissipation capacity
Bearings that run beyond their speed limits can suffer from excessive friction, increased wear, and lubrication breakdown.
2. Centrifugal Force at High Speeds
At high speeds, centrifugal forces increase significantly, especially in ball and roller bearings. This affects:
- Rolling element stability
- Cage dynamics
- Lubricant film thickness
If the centrifugal force becomes too great, it can displace the rolling elements, leading to uneven load distribution and accelerated wear.
3. Heat Generation and Thermal Expansion
Friction at high speeds generates heat, which may cause:
- Thermal expansion of bearing parts
- Breakdown of lubricants
- Sealing failures
- Cage deformation
ZNL Bearings use premium-grade lubricants and precision engineering to handle elevated speeds, but operators should always monitor operating temperature and ensure proper ventilation or cooling systems are in place.
The Load-Speed Tradeoff
Load capacity and speed performance often work against each other—boosting one can compromise the other. A bearing designed for high speed may not be suitable for heavy loads, and vice versa. Here’s how the relationship works:
- High Load + High Speed = High Risk
(Can lead to rapid failure without special materials or design) - Moderate Load + High Speed
(Best with hybrid or ceramic bearings) - High Load + Low Speed
(Ideal for taper or spherical roller bearings)
Practical Tip:
Always consult your bearing supplier (like ZNL Bearings) when your application requires a balance between load and speed. Our engineers can recommend the right product or even a custom solution.
Lubrication: The Unsung Hero
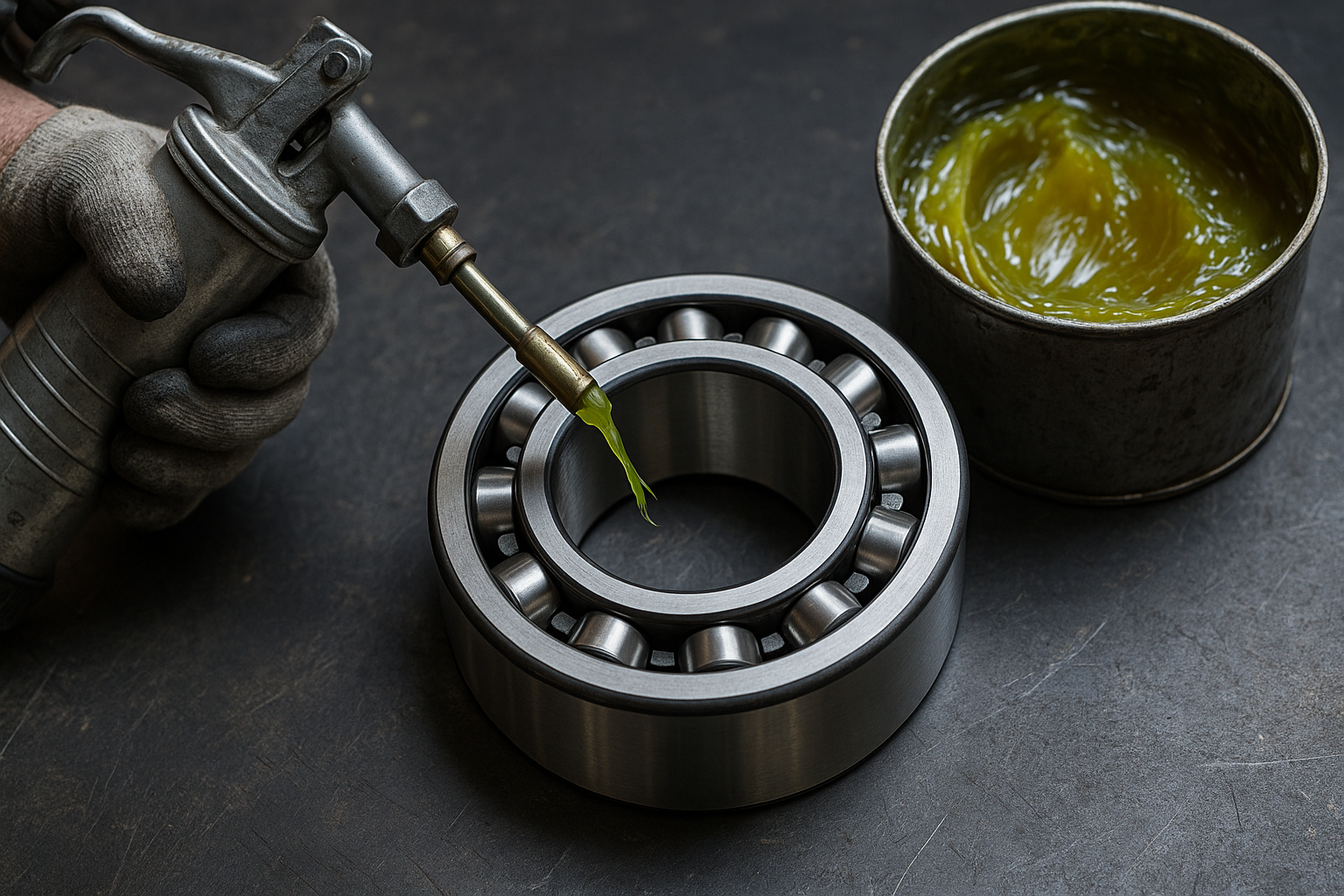

Lubrication plays a huge role in how well a bearing handles both speed and load. The right lubrication:
- Reduces friction
- Dissipates heat
- Prevents corrosion and contamination
Using the wrong lubricant or applying it improperly can negate all the benefits of a well-selected bearing.
At ZNL, our bearings with suffixes RS and ZZ come pre-lubricated with high-performance greases, and we offer guidance on re-lubrication intervals based on speed/load conditions.
How ZNL Bearings Deliver Under Load & Speed

We pride ourselves on delivering high-quality bearings that exceed international standards. Our bearings are:
- Manufactured using advanced metallurgy
- Tested under high-load and high-speed conditions
- Trusted by OEMs and industries across the globe
Whether you’re running a high-speed electric motor or a heavy-duty conveyor system, ZNL Bearings has the perfect product tailored for your operational demands.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of load and speed on bearing performance is essential for maximizing equipment life and minimizing downtime. Choosing the correct bearing type, maintaining optimal lubrication, and monitoring operational conditions can help ensure your machinery runs smoothly.
Need help choosing the right bearing for your load-speed requirements?
👉 Email or call ZNL Bearings today – we are ready to assist!